🌿 Urban Agriculture: Growing Food, Cities, and Sustainability Together
As cities expand andfarmlands shrink, the question of “how to feed urban populations sustainably” has become a global concern. The answer lies in a powerful, eco-friendly concept — Urban Agriculture (Urban Farming).
Urban agriculture means cultivating, processing, and distributing food within or around urban areas. It transforms rooftops, balconies, community spaces, and abandoned lots into productive green zones. Beyond food production, it’s reshaping cities into healthier, greener, and more resilient ecosystems.
🌱 What Is Urban Agriculture?

Urban agriculture, or urban farming, is the practice of growing crops and raising animals in
and around cities. It includes a range of activities such as:
- Rooftop gardens
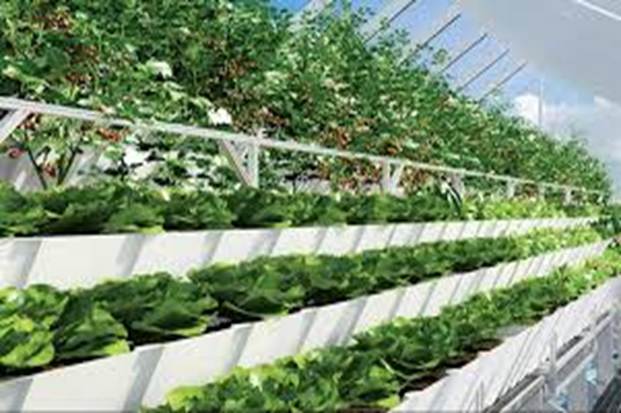
- Hydroponic and vertical farming
- Community gardens
- Backyard poultry or aquaponics
- Indoor farming using LED grow lights
Unlike traditional farming, urban agriculture is space-efficient, environmentally conscious, and community-driven.
🌿 Why Urban Agriculture Matters
By 2050, more than 68% of the world’s population will live in urban areas (United Nations report). As cities grow, food must travel longer distances — increasing carbon emissions and costs.
Urban agriculture tackles this issue head-on by bringing food production closer to consumers. It also helps cities become self-reliant and reduces the burden on rural agriculture.
🏙️ Forms of Urban Agriculture
1. Rooftop Farming
Urban rooftops are being converted into small farms where vegetables, herbs, and even fruits grow using lightweight soil and hydroponic systems. Examples can be found in New York, Tokyo, and Delhi NCR.
2. Vertical Farming
Crops are grown in stacked layers using hydroponics or aeroponics, maximizing yield in minimal space. It’s ideal for metro cities with limited land.
3. Hydroponic and Aquaponic Systems
These systems replace soil with nutrient-rich water, enabling faster, cleaner crop growth — often inside greenhouses or indoor units.
4. Community Gardens
Urban residents collectively cultivate shared spaces, improving social ties while growing organic vegetables for local consumption.
5. Backyard and Terrace Farming
Individuals grow herbs, leafy greens, or flowers on terraces or balconies — promoting food security and sustainability at a personal level.
🌾 Benefits of Urban Agriculture

🌍 1. Environmental Sustainability
- Reduces the carbon footprint by cutting food transportation distance (“food miles”).
- Helps cool urban temperatures through green roofs and vertical gardens.
- Recycles organic waste as compost, reducing landfill burden.
🥗 2. Improved Food Security
Urban farming increases local access to fresh, nutritious produce, especially in food-insecure neighborhoods.
💰 3. Economic Opportunities
- Creates employment in agri-tech, rooftop farming, equipment supply, and local distribution.
- Encourages “farm-to-table” entrepreneurship and micro-businesses.
🧑🤝🧑 4. Community Engagement
Community gardens bring people together, promoting social inclusion and collective responsibility.
❤️ 5. Health & Lifestyle Benefits
Urban agriculture provides chemical-free, organic food while encouraging people to reconnect with nature and reduce stress.
⚙️ Technologies Driving Urban Agriculture
Modern urban farming relies heavily on innovation and IoT (Internet of Things) to monitor growth conditions.
Key technologies include:
- Hydroponic and Aeroponic Systems – Grow plants without soil.
- AI-based Climate Control – Maintains temperature, light, and humidity.
- Drip Irrigation and Smart Sensors – Optimize water and nutrient use.
- LED Grow Lights – Enable 24/7 growth cycles indoors.
Startups like UrbanKisaan (India), Infarm (Germany), and Plenty (USA) are revolutionizing how cities grow food using these tools.
🏗️ Setting Up an Urban Farm: Step-by-Step
- Identify a Space:
Rooftop, balcony, basement, or unused land — anywhere with light and ventilation. - Choose a Farming System:
- Soil-based terrace farming for simplicity.
- Hydroponic or vertical farming for higher yields.
- Install Essential Infrastructure:
Containers, nutrient solutions, water systems, and grow lights (if indoors). - Select Crops:
Opt for high-value, fast-growing plants like lettuce, basil, mint, spinach, and tomatoes. - Monitor & Maintain:
Regularly check pH, light, humidity, and nutrient levels to ensure consistent growth. - Market Your Produce:
Sell to local cafes, restaurants, housing societies, or online platforms.
📊 Economic Potential
According to FAO estimates, urban agriculture can meet up to 20% of a city’s food requirements.
A 500 sq.ft rooftop can yield up to 250–300 kg of vegetables per year, reducing monthly household expenses and carbon emissions simultaneously.
With rising awareness, urban agri-startups are gaining investor attention and government support under schemes like National Urban Livelihood Mission (NULM) and Startup India.
⚠️ Challenges in Urban Agriculture

- Space Limitations:
Urban land is expensive and scarce, making large-scale operations difficult. - Initial Cost:
Setting up hydroponic or vertical farms requires investment in infrastructure and technology. - Water & Electricity Dependency:
Smart systems need regular power supply and quality water management. - Lack of Policy Support:
Many cities still lack clear regulations and incentives for rooftop or community farming. - Awareness Gap:
Urban residents often view farming as rural activity, which slows adoption.
🌏 Urban Agriculture Around the World
- Singapore: Leads in vertical farming and urban food resilience.
- Netherlands: Uses hydroponics and greenhouse tech to grow food for global export.
- USA: New York City’s “Brooklyn Grange” is one of the largest rooftop farms in the world.
- India: Cities like Bengaluru, Pune, and Delhi are emerging as urban farming hubs.
🧩 Urban Agriculture and the Future
Urban agriculture is not a luxury — it’s a necessity for climate-resilient cities.
By merging technology, sustainability, and community participation, it transforms concrete jungles into living, breathing green ecosystems.
In the coming decade, AI-powered smart farms, rooftop gardens, and hydroponic startups will redefine how cities think about food.
It’s a movement that combines environmental ethics, innovation, and self-reliance — the three pillars of the future city.
💬 Conclusion
Urban agriculture is more than just growing vegetables in a city — it’s about reconnecting urban life with nature, reducing dependency on long food supply chains, and empowering communities to be self-sufficient.
As climate change, population growth, and resource scarcity challenge humanity, urban farming stands as a symbol of resilience and hope — where every balcony, terrace, and rooftop becomes a seedbed for a greener tomorrow.
ऐसी जानकारी के लिए जाये https://investrupeya.insightsphere.in/









Post Comment